Semi-Quantitative Cell-Based Indirect Fluorescent Antibody / Qualitative Immunoblot / Quantitative Radioimmunoassay (RIA) / Semi-Quantitative Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) / Semi-Quantitative Indirect Fluorescent Antibody (IFA)
Semi-Quantitative Cell-Based Indirect Fluorescent Antibody / Qualitative Immunoblot / Quantitative Radioimmunoassay (RIA) / Semi-Quantitative Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) / Semi-Quantitative Indirect Fluorescent Antibody (IFA)
Autoimmune neurologic diseases represent a broad category of conditions characterized by immune dysregulation. Antibodies associated with these conditions may be present in the serum or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and can serve as useful markers of disease. Testing for these antineural antibodies should be considered when patients experience subacute onset of new, unexplained neurologic symptoms.
Disease Overview
Autoimmune neurologic diseases may localize to the peripheral nervous system or central nervous system (CNS). They can manifest with diverse symptoms including (but not limited to) brainstem or cerebellar syndromes, dysautonomia, encephalopathy, epilepsy, movement disorders, myelopathy, psychiatric changes, or rapidly progressive dementia. Antineural antibodies serve as useful markers of these diseases, and their detection may help establish a diagnosis, support treatment decisions, aid prognostication, serve as a prerequisite for enrollment in clinical trials, and guide the search for an associated malignancy.
For more information about laboratory testing for autoimmune neurologic diseases, including detailed information about panel test selection, refer to the ARUP Consult Autoimmune Neurologic Diseases - Antineural Antibody Testing topic.
Test Description
ARUP’s serum or CSF Autoimmune Neurologic Disease With Reflex panels can be used for the evaluation of patients with subacute onset of neurologic symptoms with possible autoimmune etiology. Testing for the presence of antineural antibodies in both serum and CSF is recommended in most situations.
These panels cover a broad range of autoimmune neurologic phenotypes; for greater diagnostic yield and improved turnaround time, consider choosing a phenotype-specific panel (see table below) rather than a broad panel.
| ARUP Panel | Test Code | |
|---|---|---|
| Serum | CSF | |
| Autoimmune Encephalopathy/Dementia Panel | 3006201 | 3006202 |
| Autoimmune Epilepsy Panel | 3006204 | 3006205 |
| Autoimmune Movement Disorder Panel | 3018964 | 3018966 |
| Autoimmune Myelopathy Panel | 3006208 | 3006209 |
| Autoimmune Dysautonomia Panel | 3006203 | — |
| Autoimmune Pediatric CNS Disorders | 3006210 | 3006211 |
Regardless of the panel chosen, order only one panel for serum and/or one panel for CSF; many antineural antibodies are redundant between these panels, and choosing based on the predominant phenotype will provide the most meaningful results. To compare these panels and the antibodies included, refer to the ARUP Antineural Antibody Testing for Autoimmune Neurologic Disease page.
Testing for individual autoantibodies is also available separately and can be used for long-term monitoring.
Antibodies Tested and Methodology
| Autoantibody Marker | Method | Individual Autoantibody or Focused Panel Test Code | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Serum | CSF | ||
| AChR binding Ab, IgGa | RIA | 0080009 | — |
| AMPAR Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA | 3001260 | 3001257 |
| Amphiphysin Ab, IgG | IB | 2008893 | 3004510 |
| ANNA-1 (Hu) | IFA, reflex IB, reflex titer | 2007961 | 2010841 |
| ANNA-2 (Ri) | IFA, reflex IB, reflex titer | 2007961 | 2010841 |
| AQP4 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 2013320 | — |
| CASPR2 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 2009452 | 3001986 |
| CV2 (CRMP-5) Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3016999 | 3017001 |
| DPPX Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3004359 | 3004512 |
| GABA-AR Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3006008 | 3006003 |
| GABA-BR Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3001270 | 3001267 |
| GAD65 Ab | ELISA | 2001771 | 3002788 |
| Ganglionic AChR Ab, IgG | RIA | 3003020 | — |
| IgLON5 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3006018 | 3006013 |
| ITPR1 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3006031 | 3006023 |
| Kelch-like protein 11 | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3018507 | 3018508 |
| LGI1 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 2009456 | 3001992 |
| Ma2/Ta Ab, IgG | IB | 3017441 | 3017440 |
| mGluR1 Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3006044 | 3006039 |
| MOG Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex titer | 3001277 | — |
| NMDAR Ab, IgG | CBA-IFA, reflex to titer | 2004221 | 2005164 |
| PCCA-1 (Yo) | IFA, reflex IB, reflex titer | 2007961 | 2010841 |
| PCCA-Tr/DNER | IFA, reflex IB, reflex titer | 2007961 | 2010841 |
| P/Q-type VGCC Ab, IgG | RIA | 0092628 | — |
| SOX1 (AGNA) Ab, IgG | IB | 3002885 | 3002886 |
| VGKC Ab, IgG | RIA | 2004890 | 3001387 |
aPerformed via reflex only, depending on the results of other autoantibody tests; refer to Reflex Patterns flowchart. Ab, antibody; AChR, acetylcholine receptor; AGNA, antiglial nuclear antibody; AMPAR, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-izoxazolepropionic acid receptor; ANNA, antineuronal nuclear antibody; AQP4, aquaporin-4; CASPR2, contactin-associated protein 2; CBA, cell-binding assay/cell-based assay; CRMP-5, collapsin response-mediator protein 5; DNER, Delta/notch-like epidermal growth factor-related receptor; DPPX, dipeptidyl-aminopeptidase-like protein 6; GABA-AR, gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor, type A; GABA-BR, gamma aminobutyric acid receptor, type B; GAD65, glutamic acid decarboxylase antibody 65-kd isoform; IFA, indirect immunofluorescence assay; Ig, immunoglobulin; IgLON5; IgLON family member 5; ITPR1, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor type 1; LGI1, leucine-rich, glioma-inactivated protein 1; mGluR1, metabotropic glutamate receptor 1; MOG, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody; PCCA, Purkinje cell cytoplasmic antibody; RIA, radioimmunoassay; SOX1, SRY-box transcription factor 1; VGCC, voltage-gated calcium channel; VGKC, voltage-gated potassium channel | |||
Reflex Patterns
Autoimmune Neurologic Disease Panel With Reflex, Serum (3018965) and CSF (3018967)
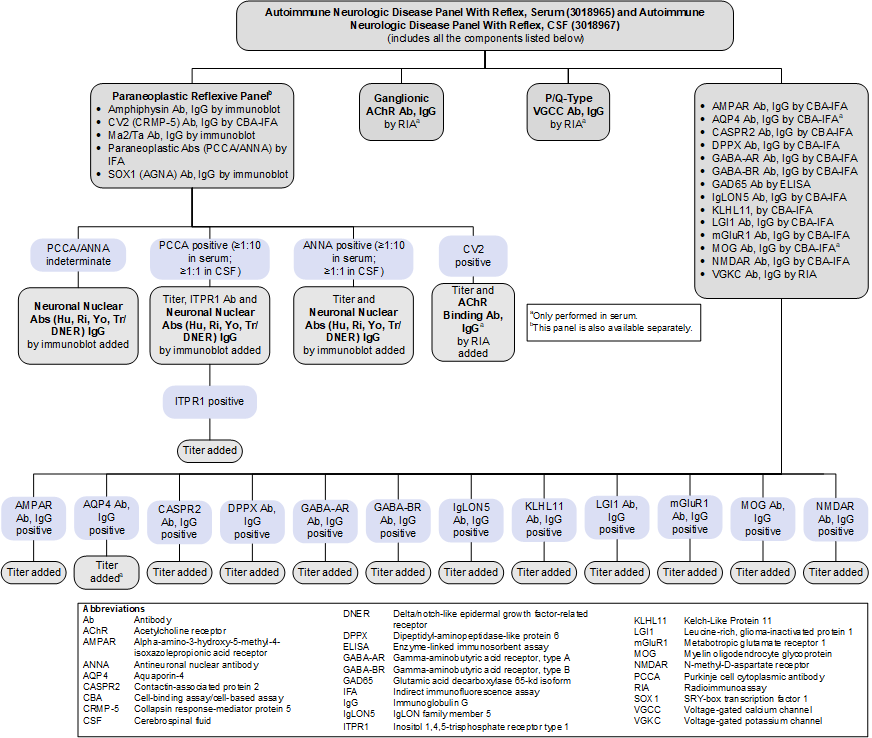
Limitations
These tests do not include all known antineural antibodies:
- Some antibodies are extremely rare or are of uncertain clinical significance.
- As testing for newly described antibodies becomes available and their clinical relevance is established, these panels will evolve to reflect these discoveries.
Test Interpretation
Results
Results must be interpreted in the clinical context of the individual patient; test results (positive or negative) should not supersede clinical judgement.
| Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Positive for ≥1 autoantibodies | Autoantibody(ies) detected May support a diagnosis of autoimmune neurologic disease Consider a focused search for malignancy based on antibody-tumor associations |
| Negative | No autoantibodies detected A diagnosis of autoimmune neurologic disease is not excluded |
References
-
33221892
Budhram A, Dubey D, Sechi E, et al. Neural antibody testing in patients with suspected autoimmune encephalitis. Clin Chem. 2020;66(12):1496-1509.


 Feedback
Feedback